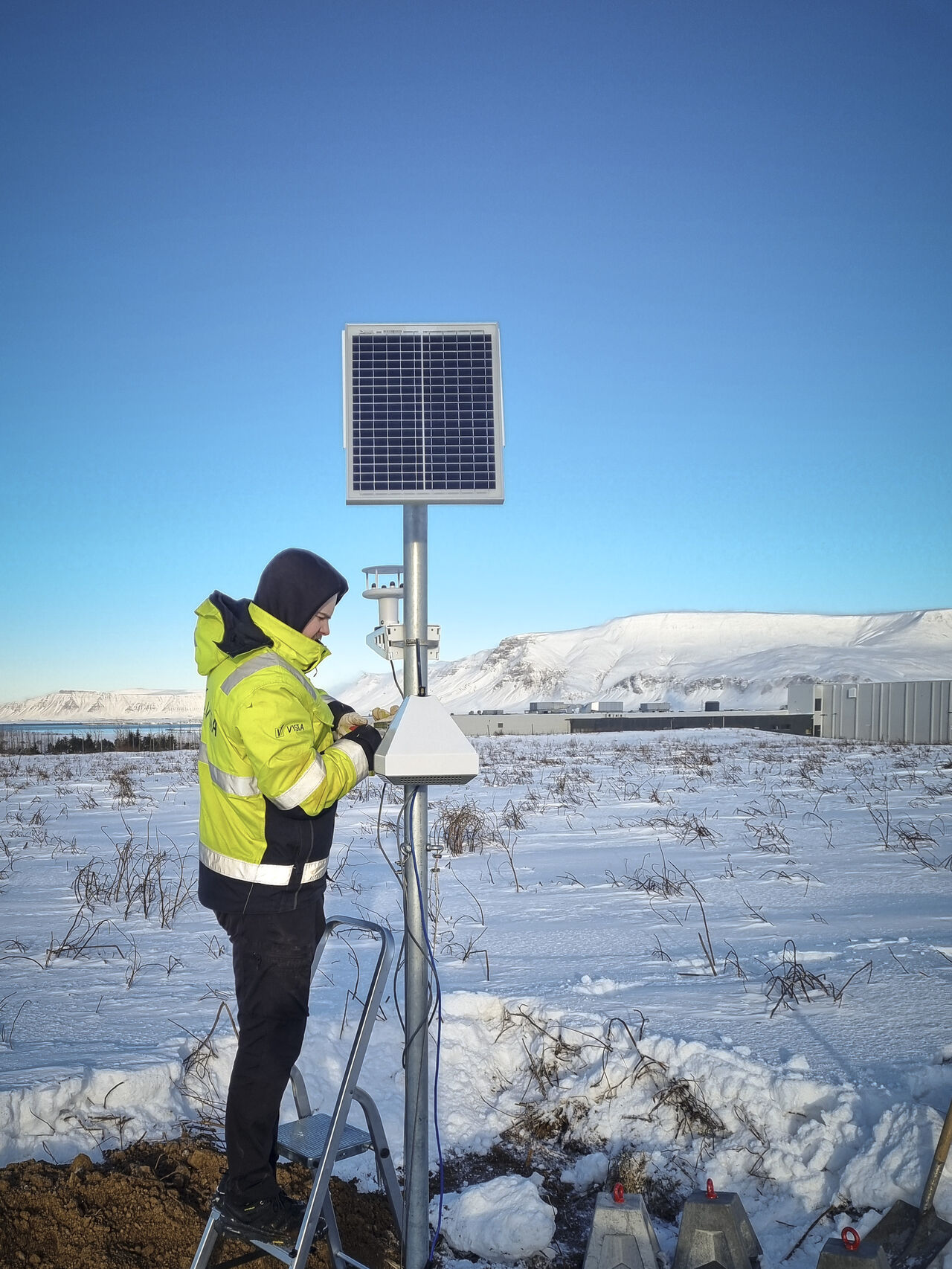
 A UK local authority installed nine AQMesh systems at different points across a busy town, measuring nitrogen dioxide (NO2) at 15 minute intervals, monitoring 24/7. These locations were established monitoring points, where measurements had been taken previously using diffusion tubes, limited to one average reading every few weeks.
A UK local authority installed nine AQMesh systems at different points across a busy town, measuring nitrogen dioxide (NO2) at 15 minute intervals, monitoring 24/7. These locations were established monitoring points, where measurements had been taken previously using diffusion tubes, limited to one average reading every few weeks.
AQMesh – in common with all lower cost air quality systems – can provide near real-time air quality information, with high frequency measurements that allow daily and weekly patterns to be seen. However such systems are not certified, as are reference stations or diffusion tubes. As a result, AQMesh readings need to be ‘calibrated’ against certified readings, at some point in the network, to provide confidence in data accuracy and traceability to an approved standard.
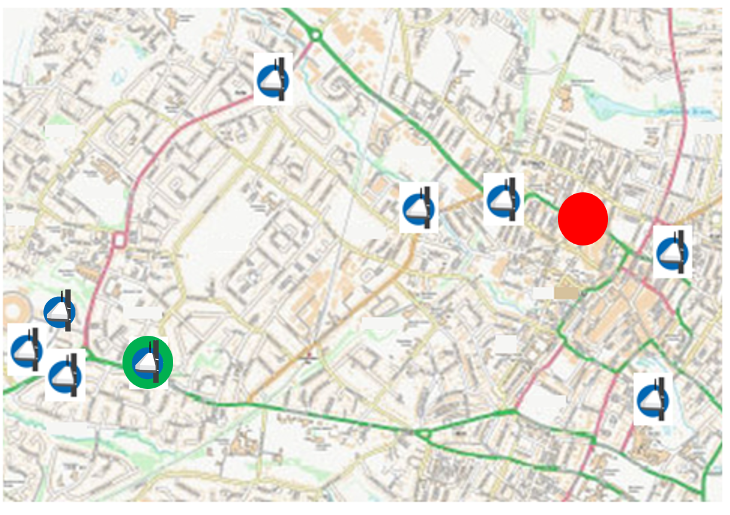
Typically such ‘calibration’ is carried out by mounting at least one AQMesh ‘pod’ very close to a reference station, so pod and reference are sampling the same air and readings can be compared. However this approach does require staff to move pods from position to position, which can be time-consuming and therefore costly. An alternative approach was used for this network, similar to the one developed by the University of Cambridge and used in a major project in London (Breathe London pilot). One of the authority’s reference stations (location in red on map) was used to ‘calibrate’ the network of pods and the other (location in green on map) was used to cross-check network accuracy.
AQMesh network deployment (BELOW): AQMesh locations marked in blue, reference station used for calibration in red, reference station used for control co-location in green
The four-month project demonstrated that the AQMesh network showed that stakeholders could have the same high confidence in readings when the network was calibrated remotely as when pods were co-located for calibration (the gold standard for this technology), but with significant savings in field support and reduced data loss.
For more information or to discuss how AQMesh can help with your air quality monitoring contact us today.




